Welcome to an in-depth analysis of how cultural background shapes treatment options in mental health. This guide explores the significant role that cultural identity plays in therapeutic approaches, emphasizing the necessity of integrating cultural considerations into mental health practices for effective and respectful care.
How Cultural Background Shapes Treatment Options
Culture encompasses the shared values, norms, beliefs, and practices that shape individuals’ worldviews and behaviors, significantly influencing mental health treatment. But why is understanding this impact so crucial for mental health professionals?
Why Does Cultural Background Shape Treatment Options?
Cultural background influences every aspect of mental health care, from diagnosis to therapy modalities and patient engagement strategies. When therapists comprehend and integrate the cultural dynamics of their patients, treatment becomes more personalized and effective, leading to better outcomes. This understanding is foundational for developing cultural competence, which involves recognizing and appropriately responding to the cultural differences that significantly affect the therapeutic process.
Achieving Cultural Competence in Mental Health Care
Achieving cultural competence is essential for providing care that respects and effectively addresses diverse cultural needs. The American Psychological Association’s guidelines offer frameworks for therapists, emphasizing the need to understand diverse cultural perspectives and treatment preferences. How do professionals develop these skills? They engage in continuous education about different cultural practices and health beliefs, which is crucial for enhancing their ability to deliver culturally competent care.

Cultural Background’s Impact on Treatment Strategies
How Do Cultural Differences Affect Diagnosis and Treatment?
Cultural differences can lead to variations in how mental disorders are diagnosed and treated. For example, some cultures may express depression through physical rather than emotional symptoms, which can affect diagnostic accuracy. Therapists must use culturally sensitive diagnostic tools and consider these cultural expressions during the assessment process. Research available through PubMed illustrates various culturally adapted treatment methods that acknowledge and incorporate these differences effectively.
Tailoring Therapy to Cultural Needs
Adapting therapy modalities to fit cultural contexts involves understanding the patient’s cultural background and integrating this knowledge into the treatment process. This might include using language that resonates with the patient, considering family dynamics, and incorporating culturally significant healing practices. Articles on ScienceDirect discuss how therapies like Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) are often modified to better align with the patient’s cultural context.
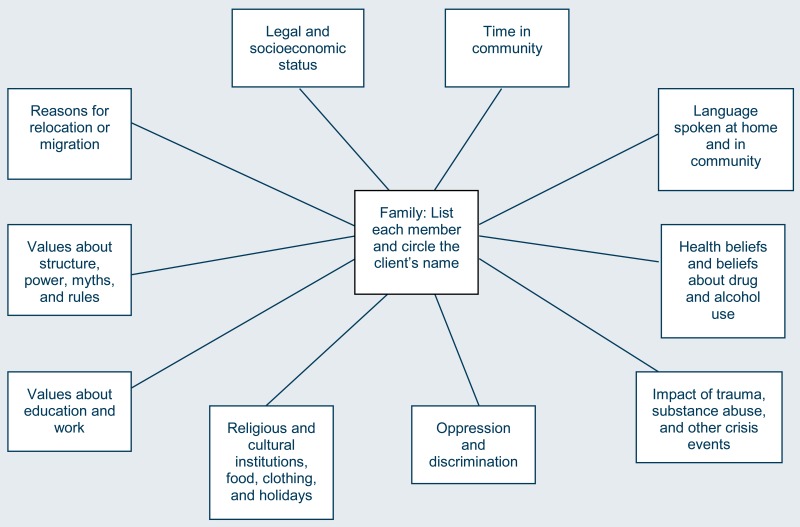
Case Study: Cultural Barriers in Therapy
Background: Consider the case of Maria, a young Latina woman who sought therapy for depression and anxiety. Her cultural background emphasized familial obligations and collective well-being, which shaped her experience and expression of mental health issues.
Challenges and Strategies:
- Stigma and Cultural Misalignment: Maria initially struggled with therapy due to cultural stigma and a mismatch between her values and the therapeutic approaches focused on individualism.
- Inclusive Family Therapy Sessions: The therapist invited Maria’s family members to certain sessions to educate them about mental health and to align the treatment with Maria’s cultural values.
- Cultural Competency Training for Therapists: Maria’s therapist undertook further training in cultural competency, enhancing understanding of Latino values and integrating these insights into the therapy process.
Outcomes: These culturally adapted strategies improved Maria’s engagement with therapy and her overall mental health outcomes.
Conclusions: Cultural Background Shapes Treatment Options
Understanding and integrating cultural considerations in mental health treatment is essential for developing effective, inclusive care. By addressing the specific cultural dynamics of patients, therapists can provide more effective and supportive care.


