Welcome to a journey into one of the most tantalizing questions in physics: Can anything travel faster than light? This detailed exploration dives into the theories of relativity, quantum mechanics, and cutting-edge scientific research to explore the limits of how fast things can move in our universe. Join us as we unravel historical theories, contemporary experiments, and the theoretical possibilities that challenge our current understanding of the speed of light.
Understanding the Speed of Light
The speed of light in a vacuum, commonly denoted as “c,” is approximately 299,792 kilometers per second. It is not only a key constant in physics but also a speed limit according to Einstein’s theory of relativity.
What is Special About the Speed of Light?
According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, the speed of light is the ultimate speed limit for any object with mass. This theory asserts that as an object with mass approaches the speed of light, its relativistic mass increases, requiring infinite energy to reach or exceed the speed of light.
Historical Context and the Establishment of Light’s Speed Limit
The establishment of the speed of light as a constant came from the work of James Clerk Maxwell and was further solidified by Albert Einstein’s special relativity theory. These developments framed our understanding that the speed of light is not just a barrier but a fundamental property of the universe.
Challenging the Speed of Light: Theoretical Exceptions and Anomalies
While the speed of light is a cornerstone of modern physics, several theoretical exceptions suggest possibilities for “faster-than-light” phenomena.
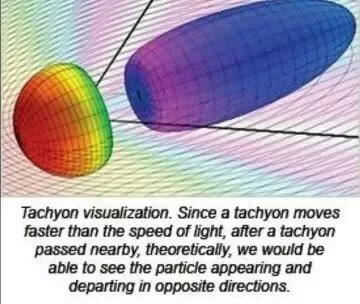
Tachyons: Hypothetical Faster-Than-Light Particles
Tachyons are hypothetical particles that, if they exist, would move faster than light. The theory proposes that these particles have imaginary mass and can only exist at speeds greater than that of light. However, tachyons remain a speculative concept with no experimental evidence to support their existence.
Quantum Entanglement and Information Transfer
Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where two particles become linked, and the state of one (no matter how far apart) can instantly influence the state of the other. Some interpretations suggest that this involves information transfer faster than light, although this remains a topic of debate among physicists.
Warp Drives and Theoretical Propulsion Systems
The concept of a warp drive, popularized by science fiction, involves bending space-time to allow faster-than-light travel within a “warp bubble.” This theoretically would enable travel faster than light without violating relativity.
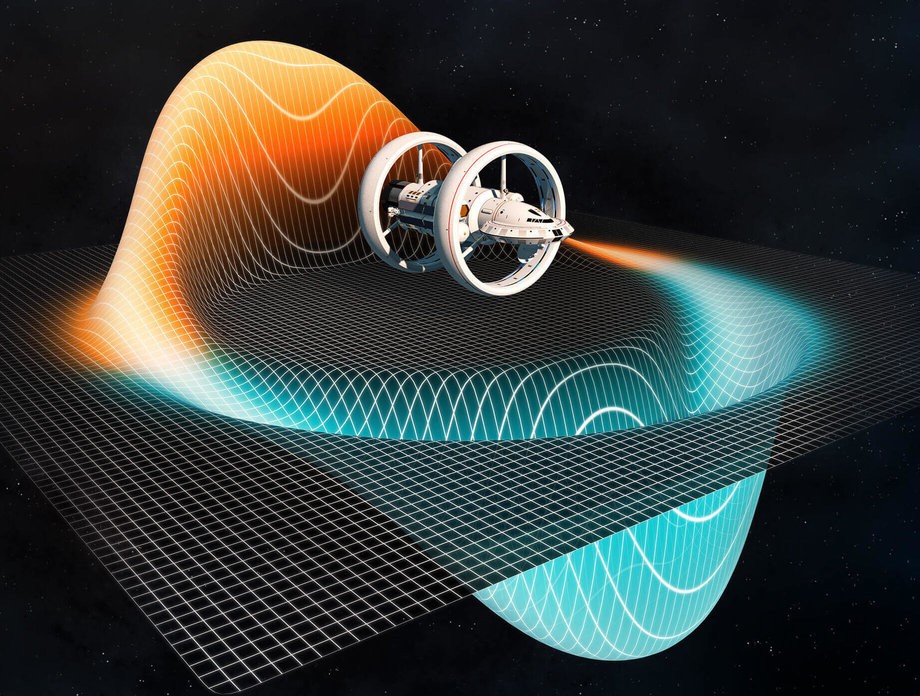
Alcubierre Drive: Warping Space-Time
Proposed by physicist Miguel Alcubierre in 1994, this concept involves expanding the fabric of space behind a spacecraft and contracting it in front, effectively moving the craft faster than light. The energy requirements and practicalities of creating such a drive are immense, with current technology far from achieving this.
Philosophical and Practical Implications of Faster-Than-Light Travel
What Would Faster-Than-Light Travel Mean for Humanity?
Exploring the potential for faster-than-light travel opens profound philosophical and practical questions about space exploration, time travel, and our place in the universe. It challenges the very notions of causality and time as understood by classical physics.

Ethical Considerations of Breaking Physical Limits
As theoretical physics progresses towards possibilities like warp drives or tachyons, ethical considerations must be addressed. These include the implications of time travel, the alteration of space-time, and the potential risks associated with high-energy experiments.
Concluding Thoughts: The Ongoing Pursuit of Superluminal Speeds
Can anything travel faster than light? While current scientific understanding and evidence suggest that the speed of light remains the universal speed limit, ongoing research into quantum mechanics, particle physics, and cosmology continues to push the boundaries of what might be possible. For those interested in following the latest developments in this fascinating field, reputable journals and websites like those found through NASA’s Astrophysics Data System offer a wealth of up-to-date information.


